Rain Attenuation
Overview
Rain calculations are available in conventional microwave and adaptive modulation applications. Rain attenuation does not usually contribute to the overall link unavailability at frequencies below 8 GHz; however, this will depend on the path length and the geographic location of the path. The user is responsible to enable the rain calculation.
A rain calculation consists of the two basic parts:
- Calculate the rain rate (millimeters / hour) which will produce an attenuation equal to the link fade margin
- Determine the fraction of time that this rain rate is exceeded i.e. the probability of an outage due to rain
- Rain affects both directions of transmission simultaneously and is a function of frequency, path length and polarization.
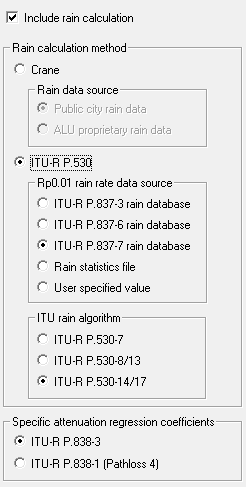
Calculation Method
Rain calculations can be made using the Crane or ITU-530 algorithms. The choice is made under Configure - Options - Calculation Options - Transmission calculations - Rain.
The Crane method requires a rain statistics file (a table of rain rate and the percent of time that the rain rate is exceeded).
The ITU method only requires the rain rate which is exceeded for 0.01% of the time. This in turn can be obtained from the following sources:
- ITU-R P837 rain database
- rain statistics file
- user specified rain rate
The regression coefficients α and β can be computed from ITU-R-838-1 or 838-3. The former uses a table of values and a logarithmic interpolation procedure. The latter uses analytic equations. Slight differences occur between the two methods. Pathloss version 4 used 838-1.