Path Profile Data Entry Form - Common Parameters
The first eight lines in the path profile data entry form are common to all multipath fade algorithms.
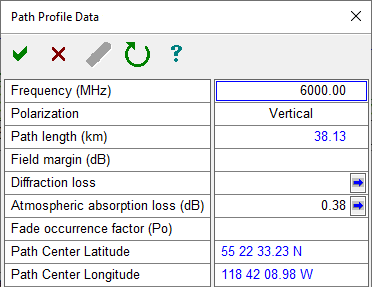
Frequency
This is the design frequency used throughout the program and is usually the band center of the frequency plan.
Polarization
Currently only horizontal and vertical polarization are actually used in the program.
Path length
If a path profile exists, the path length is calculated as the actual distance of the ray path at K = 4/3. The calculation takes into account the elevation differences of the two sites. If a path profile does not exist, the path length is calculated from the coordinates. In either of these cases, the path length cannot be edited; otherwise, any value for the path length can be entered. If you are calculating performance as a function of path length, create a new file. Select Files - New on the menu bar.
Field margin
Field margin is a safety factor to account for the long term degradation of connectors and antenna orientation in a practical installation. A typical value would be in the order of 1 to 2 dB.
Diffraction loss
Diffraction loss calculations are normally carried out in the Diffraction module and are not automatically transferred to the Transmission Analysis module If a diffraction calculation exists and the value is different from the value in the Transmission Analysis, the user is prompted to update the Transmission Analysis with the new calculated value. The Diffraction section is used for a variety of different analysis and there is no way of determining whether a diffraction loss calculation should be included in the Transmission Analysis. The question "When should diffraction loss be included in the analysis?" arises here. Suppose a link has 6 dB of diffraction loss at K = 4/3 and no diffraction loss (free space loss) at K = 5. Multipath fading typically occurs at high values of K and therefore, free space loss conditions exist during the fading and the diffraction loss should not be considered for the reliability calculation.
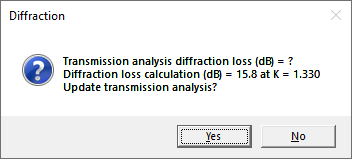
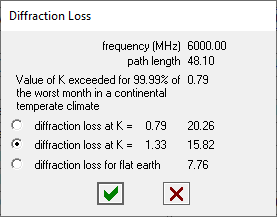
The diffraction loss calculate button in the path profile data entry form provides a convenient method of examining / entering a diffraction loss value. Values are calculated and displayed for the minimum value of K based on the path length, the median value of K and a K of infinity.
Atmospheric Absorption Loss
The loss due to water vapor and oxygen in the atmosphere. More on Atmospheric Absorption
Fade occurrence factor (Po)
The worst month multipath fade probability is given by the expression P = Po * pow(10, -A/10) where A is the fade margin.
Path center latitude and longitude.
If site coordinates have been entered, these are the average values of the two sites and cannot be edited. Path center coordinates are required to access geographic data such as average annual temperature.